

Recently, however, some authors have reported damaging effect of therapeutic radiation on cardiac pulse generators. It was previously thought that diagnostic or therapeutic ionizing radiation did not have an adverse effect on the function of cardiac pacemakers. Cautions should be taken for pacemaker-dependent patients.
CARRIER COMMAND 2 SONIC PULSE GENERATOR UPGRADE
Electrosurgery during PG replacement or upgrade surgery can trigger output failure or inappropriate low pacing rate in certain models of modern pacemakers. No electrosurgery-related malfunction was found in MAUDE database on 862 pacemaker malfunction cases during the same period from other vendors. The majority of these (78.5%) occurred during PG replacement at ERI or upgrade surgery. The distribution of adverse events was loss of pacing (59.5%), reversion to backup pacing (32.4%), inappropriate low pacing rate (5.4%), and ventricular fibrillation (2.7%). Twenty-four cases (65%) had output failure or inappropriate low pacing rate. During the same period, 1174 cases of pacemaker malfunctions were reported on the same models in MAUDE database, 37 of which (3.2%) were electrosurgery-related.

Four patients (0.3% of all patients), all with pacemakers from St Jude Medical (2.8%, 4 of 142) had output failure or inappropriately low pacing rate below 30Â bpm during electrosurgery, despite being programmed in an asynchronous mode.
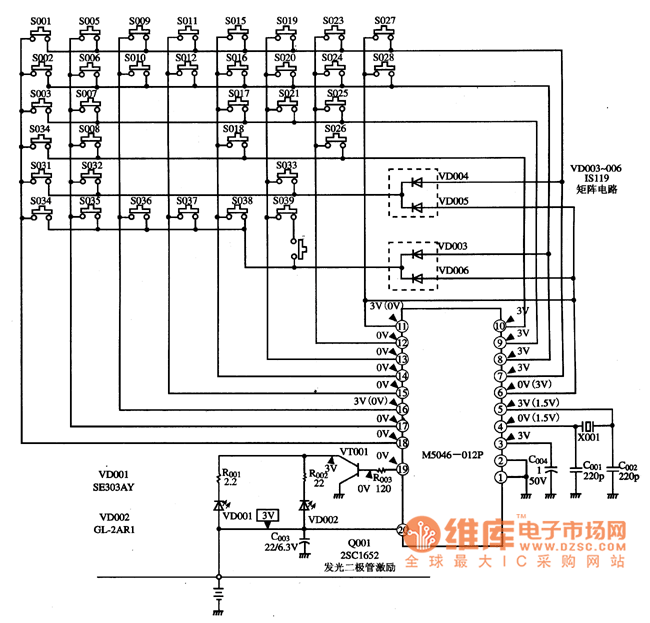
A total of 1398 consecutive patients from 2 large tertiary referral centers in Minneapolis, MN undergoing PG replacement or upgrade surgery were retrospectively studied. The occurrence of this pacemaker malfunction was then studied by using MAUDE database for all four major device vendors.
CARRIER COMMAND 2 SONIC PULSE GENERATOR GENERATOR
A retrospective study was conducted to investigate electrosurgery-related pacemaker malfunction in consecutive patients undergoing pulse generator (PG) replacement or upgrade from two large hospitals in Minneapolis, MN between January 2011 and January 2014. The aim of this study is to investigate the frequency of electrosurgery-related pacemaker malfunction. Lin, Yun Melby, Daniel P Krishnan, Balaji Adabag, Selcuk Tholakanahalli, Venkatakrishna Li, Jian-Ming 870.3610 Section 870.3610 Food and Drugs FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION, DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES.įrequency of pacemaker malfunction associated with monopolar electrosurgery during pulse generator replacement or upgrade surgery. 21 Food and Drugs 8 false Implantable pacemaker pulse generator. asynchronous devices implanted in the human body. External programmable pacemaker pulse generator. 870.1750 Section 870.1750 Food and Drugs FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION, DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN. 21 Food and Drugs 8 false External programmable pacemaker pulse generator. An implantable pacemaker pulse generator is a device that has.Ģ1 CFR 870.1750 - External programmable pacemaker pulse generator. 870.3610 Section 870.3610 Food and Drugs FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION, DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES. implantable pacemaker pulse generator device that was in commercial distribution before May 28, 1976, or that. An implantable pacemaker pulse generator is a device that has. 21 CFR 870.3610 - Implantable pacemaker pulse generator.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
