
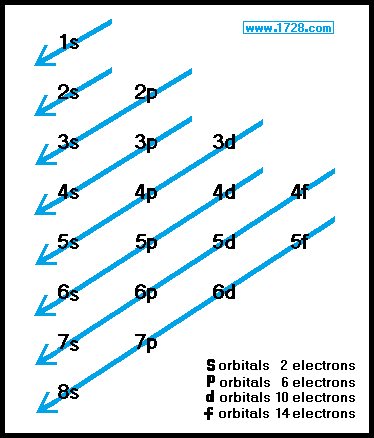
The total number of arrows in the notation will equal the atomic number. Remember, according to Hund's Rule, each of the 2p orbitals will receive one electron (up-facing arrow) before any will get a second electron (down-facing arrow). Note that the first arrow of each orbital is up-facing. Electron configurations of atoms follow a standard. Electron configuration The arrangement of electrons. The order of the orbitals being filled can be determined by looking at the orbital chart below. The electron configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. Electron orbitals the different energy levels filled by electrons within an atom (s, p, d, and f). Each electron is represented as either an up-facing arrow or a down-facing arrow. The electrons are drawn in on blanks representing the orbitals. The second system of notation is called orbital notation. The total of the superscripts will always be equal to the atomic number of the element when the notation is properly written. All the elements can have their electron arrangements listed in this way. This electron is placed in the first p orbital. There are guidelines for determining the electron configuration of an atom. An orbital diagram is used to determine an atoms electron configuration. Within each shell, the s subshell is at a lower energy than the p.
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)
There are four different orbital shapes: s, p, d, and f. The last electron to be placed in an atom of boron is also in the second energy level. In a more realistic model, electrons move in atomic orbitals, or subshells. Usually, only the valence or outermost electrons are involved in chemical. The 2s orbital contains two electrons (its maximum). Chemical properties depend on the number and arrangement of electrons in an atom. Watch Out Memorize the order of orbital filling (or just. The first orbital to receive any electrons in this level is an s orbital. Electrons will always occupy the lowest available energy level first. The next energy level being filled is the second energy level, shown by the 2 in the notation. The type of orbital in the first energy level is an s orbital. The 1 on the left tells you that the first energy level is being used. The electrons are arranged in four subshells namely s,p, d and f. Chemists commonly use two systems of notation to show the electron placement in an atom. Electron Configuration describes how the electrons are distributed in an atoms orbitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
